Imaging Language Decoded
If your doctor has told you to get a medical imaging test, that can be an understandably stressful position to be in. Medical jargon can be confusing enough, but with medical imaging being such a high-tech field, it can often be even more difficult to understand what the test entails and how it will impact your body. This guide is designed to help you more easily understand the various terms of medical imaging and how this powerful medical tool can be used to help you stay healthy.
Here’s a look at some words you may come across when considering a medical imaging test:
Biopsies and aspirations
These procedures help your doctor to take a closer look at a mass or cyst on the body. We use ultrasound-guided biopsies to remove a small amount of tissue from the mass, which we then send to pathology for evaluation. Aspiration uses a thin needle and syringe, with the guidance of an ultrasound, to remove liquid from a mass or cyst for evaluation. We will use an injected anesthetic to numb the area before taking a biopsy or aspiration. You may experience some discomfort, but it should not be painful. Results are available within 24-48 hours and will be sent directly to your doctor.
Bone density test
A bone density test uses a low dose X-ray to identify osteopenia (slight bone loss) or osteoporosis (porous bone). Our X-ray technician will take images of the lumbar spine and least dominant inner hip bone, where density issues are easiest to spot. These sites are also the best locations to monitor how the therapy your doctor ordered is working. An X-ray of both spine and hip should take no more than 10 minutes, and you should not feel any pain.
Cardiovascular stress test
A stress test helps your doctor determine if chest pain or other symptoms are related to heart disease. This test uses an echocardiogram, also known as a stress echo or SE. This ultrasound imaging of the heart looks at heart wall motion in response to physical stress. Images of the heart are taken “at rest” to acquire a baseline at a resting heart rate. The patient then walks on a treadmill or other exercise equipment to increase the heart rate. Images of the heart are taken during this activity, or “at stress,” to assess heart wall motion at the peak heart rate. Comparing your heart in these two states can give your doctor a closer look at your heart health.

CT Scan
A CT scan, also called X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT), uses X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional, virtual “slices” of specific areas of a scanned object, allowing the radiologist to see inside the object without cutting.
Mammography
This can take one of two forms: a screening mammogram takes four images, two of the right breast and two of the left breast. This test is typically done as a preventative measure and simply looks for any mass or nodule that may be cause for concern. If a mass is found, your doctor may order a diagnostic mammogram. The diagnostic mammogram uses additional images to give a more complete view of the mass.
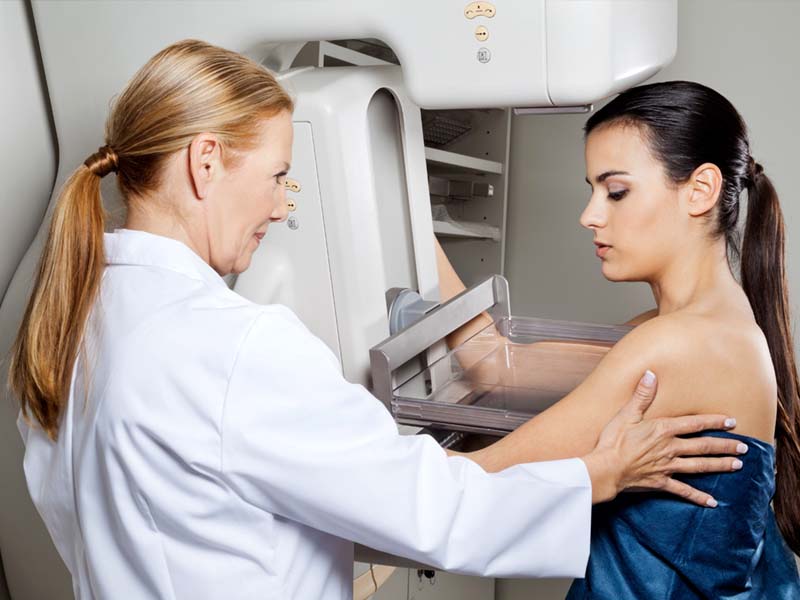
The study is very quick; the entire appointment, including changing in and out of your clothes, takes no more than 30 minutes, and the exam itself is 7-10 minutes. The mammogram is not supposed to be painful but may be uncomfortable for some women. The portion of the exam that involves compression is very short, lasting only a few seconds.
MRI/MRA
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a strong magnet and radio waves to align water molecules in the area being imaged. Because our bodies are made up of mostly water and each organ has different quantities of water in it, the images acquired show differences in normal and abnormal anatomy. An MRA (magnetic resonance angiography) produces pictures of the arteries to evaluate them for abnormal narrowing or aneurysms. MRA is often used to look at arteries in the neck and brain, inside the heart, in the renal arteries, and in the legs. In short, both MRI and MRA images generate a 3D image that can help the radiologist find abnormalities. This 3D image creation is called digital geometry.
Nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine is a branch of radiology that involves administering small amounts of radioactive material (called radiopharmaceuticals or radiotracers) into the body by injection, inhalation, or pill. The medication accumulates in a particular organ or area of the body, where it gives off energy in the form of gamma rays. The energy can then be viewed by a special camera that produces a series of images on a computer screen. This can provide details about the structure and function of an organ, tissue, or bone in the body. It also can help identify abnormalities early in the progression of a disease.
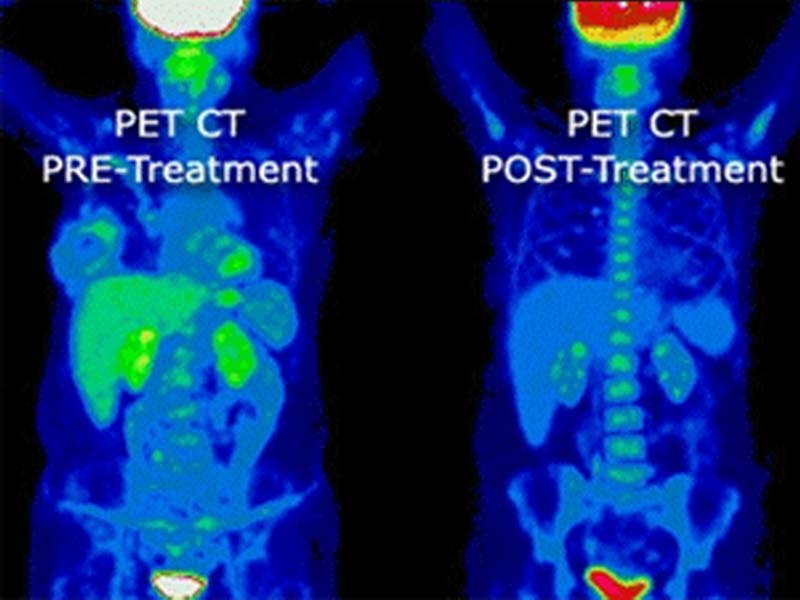
PET/CT Scan
This is a diagnostic imaging study that combines the best features of positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT). PET scans can pinpoint a disease on the cellular level, and CT scans record images of the body, focusing on specific sections from various views. Together, they can produce a series of images that don't show up on conventional scans.
Ultrasound
If you’re a parent, you may already be familiar with this term. Ultrasound technology has many applications beyond obstetrics. Ultrasounds are used to see inside the body and can closely examine tendons, muscles, joints, vessels, and internal organs. Using high-frequency sound waves, the radiologist can often determine the source of a disease or can rule out certain causes. Ultrasound is usually the first line of imaging in determining the source of disease. Additional imaging, such as CT, MRI, or mammography, may be recommended.
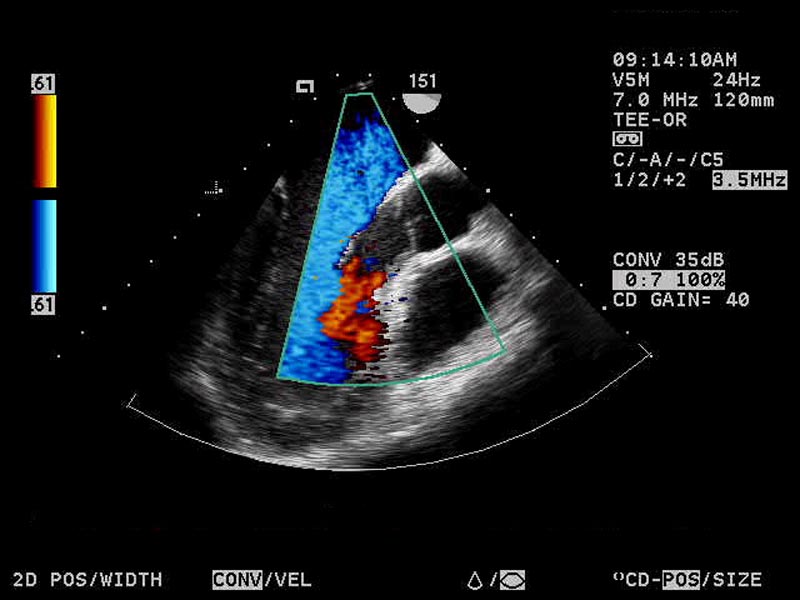
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart and is referred to as an echo. It can use 2D, 3D, and Doppler technology to create images of the heart. It is used to diagnose, manage, and monitor progress of patients who have problems or are suspected of having problems with their heart.
X-ray
This important medical tool can detect issues with the skeleton, from broken bones to detecting some diseases in soft tissue. Chest X-rays are very common, as they help doctors identify pneumonia, lung cancer, and pulmonary edema. The abdominal X-ray can detect intestinal obstruction or can locate problematic free air and free fluid. X-rays may also be used to detect issues such as gallstones or kidney stones, which are often but not always visible.
When getting a medical imaging scan or test, the person performing the test should explain what they are doing and make every effort to make you feel comfortable. Knowing what to expect can go a long way toward making you feel better about the entire process.


